For individuals struggling with obesity and seeking a long-term solution for weight loss, gastric bypass surgery is a well-established option. However, there are different approaches to this surgery, with the two most common being the traditional gastric bypass and the mini gastric bypass. While both procedures share the same goal of helping patients achieve significant weight loss, they have distinct differences that are worth exploring to determine which might be the most suitable for each patient’s unique needs.
Here is a table highlighting the differences between Mini Gastric Bypass and Traditional Gastric Bypass:
| Aspect | Mini Gastric Bypass | Traditional Gastric Bypass |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Procedure | One-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB) | Roux-en-Y gastric bypass |
| Stomach Pouch | Smaller pouch at the top of the stomach | Smaller pouch at the top of the stomach |
| Connection to Small Intestine | Connected to a lower point in the small intestine | Connected directly to a lower portion of the small intestine |
| Restriction | Primarily relies on restriction for weight loss | Achieves weight loss through both restriction and malabsorption |
| Malabsorptive Effects | Some malabsorptive effects, but less pronounced | Significant malabsorptive effects due to a larger bypassed portion of the small intestine |
| Weight Loss Effectiveness | Effective for significant weight loss | Effective for substantial weight loss |
| Improvement in Health Conditions | Can improve obesity-related health conditions | Can improve obesity-related health conditions |
| Reversibility | In some cases, may be reversible | Generally considered irreversible |
| Surgical Complexity | Generally considered less complex | More complex surgical procedure with multiple incisions |
Please note that the choice between the two procedures should be made after consultation with a healthcare professional and careful consideration of individual health and weight loss goals.
Before delving into the differences, let’s first understand the fundamental principles of gastric bypass surgery. This type of surgery is considered a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure. The main objective is to reduce the size of the stomach and reroute the digestive tract to limit food intake and nutrient absorption.
Traditional Gastric Bypass:
- Procedure: In a traditional gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, a surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach. This pouch is then connected directly to the small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine.
- Restriction and Malabsorption: Traditional gastric bypass achieves weight loss through both restriction and malabsorption. The reduced stomach size restricts food intake, while bypassing a portion of the small intestine reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients.
- Effectiveness: This procedure is known for its effectiveness in promoting substantial weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
- Reversibility: Traditional gastric bypass is generally considered irreversible due to the permanent changes made to the digestive tract.
- Surgical Complexity: It is a more complex surgical procedure that involves multiple incisions and requires a high level of surgical expertise.
Mini Gastric Bypass:
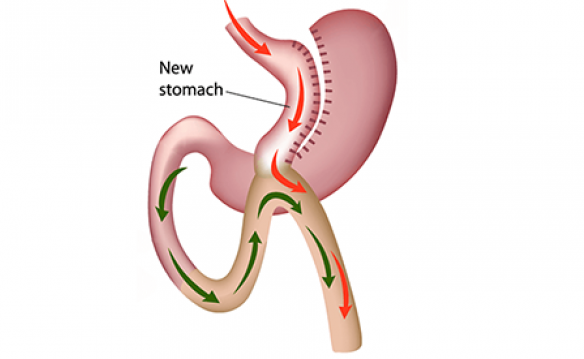
- Procedure: In contrast, the mini gastric bypass, also known as the one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB), involves creating a smaller stomach pouch and connecting it to a lower point in the small intestine, thus bypassing less of the small intestine compared to the traditional bypass.
- Restriction and Malabsorption: Mini gastric bypass primarily relies on restriction for weight loss. While it does have some malabsorptive effects, they are less pronounced than in the traditional procedure.
- Effectiveness: Mini gastric bypass has been shown to be effective in achieving significant weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions.
- Reversibility: In some cases, the mini gastric bypass may be reversible, depending on the surgeon’s approach and the specific anatomy of the patient.
- Surgical Complexity: Mini gastric bypass is generally considered less complex than the traditional gastric bypass, as it involves fewer incisions and a shorter surgical duration.
Choosing Between the Two:
The choice between traditional and mini gastric bypass depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health, body mass index (BMI), and personal preferences. Some key considerations include:
- Weight Loss Goals: Patients with higher BMI and more significant weight loss goals may opt for the traditional gastric bypass due to its greater malabsorptive effects.
- Risk Tolerance: The mini gastric bypass is considered a less risky procedure, which may make it a preferred choice for patients with certain health concerns.
- Reversibility: Patients who desire the option of reversibility may lean towards the mini gastric bypass.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: It’s essential to choose a surgeon experienced in the specific procedure, as their skill greatly influences the surgery’s success.
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical evaluation and consultation with a bariatric surgeon are critical in determining the most appropriate procedure.
In conclusion, both traditional and mini gastric bypass surgeries are effective options for weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions. The choice between the two should be made after careful consideration, consultation with healthcare professionals, and an understanding of the unique characteristics of each procedure. Ultimately, the goal of either surgery is to help individuals achieve a healthier, happier, and more active life.