Cancer
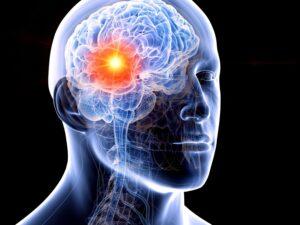
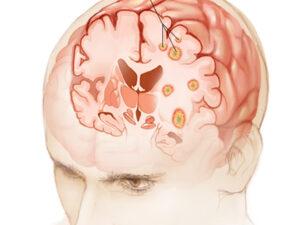
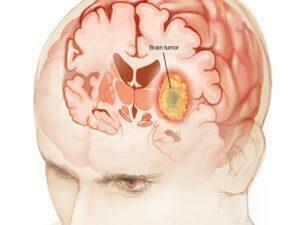
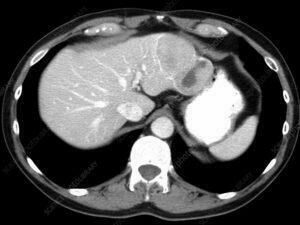
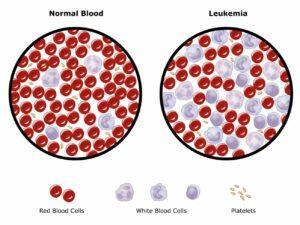
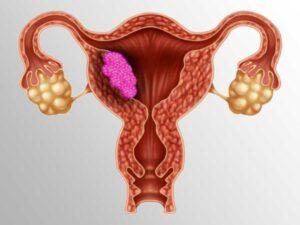
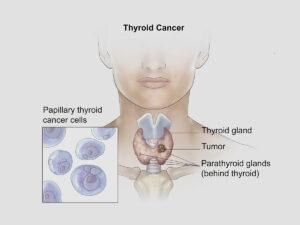
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. It occurs when the body’s cellular regulatory mechanisms malfunction, leading to an imbalance in cell production and death. This results in forming of a mass of cells called a tumor, which can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
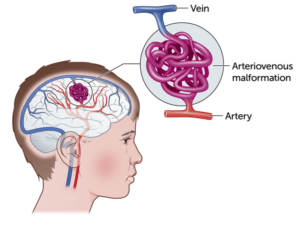
The root cause of cancer is genetic mutations within cells, which can be inherited, induced by environmental factors, or occur spontaneously. These mutations affect genes that regulate cell growth and division, leading to cancer development. Cancer risk factors include age, family history, exposure to carcinogens (such as tobacco, radiation, and certain chemicals), and certain infections like human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis.
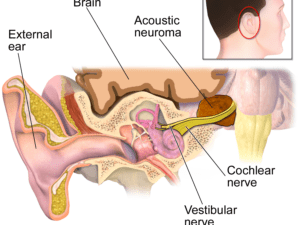
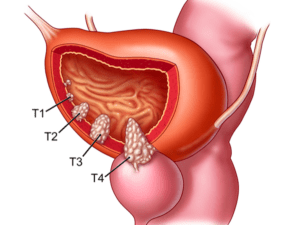
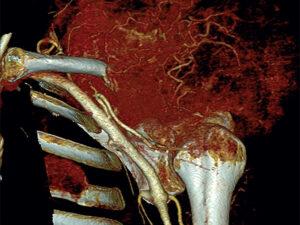
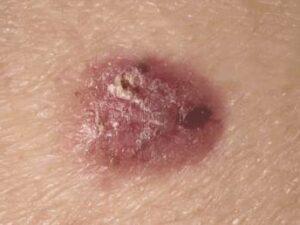
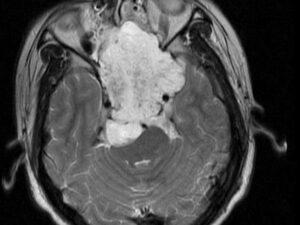
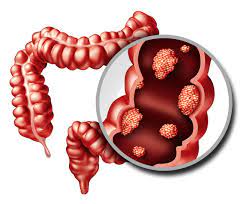
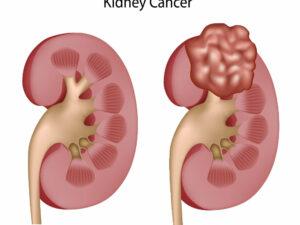
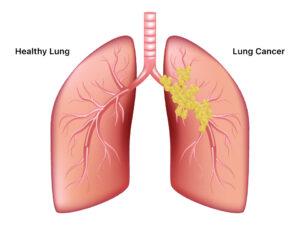
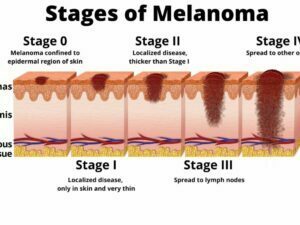
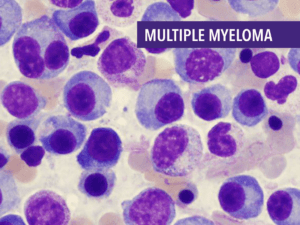
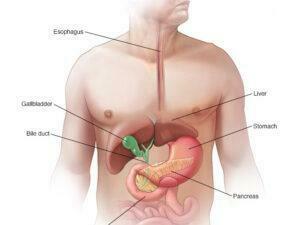
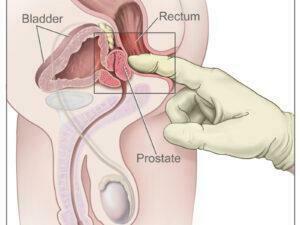
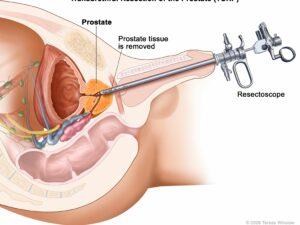
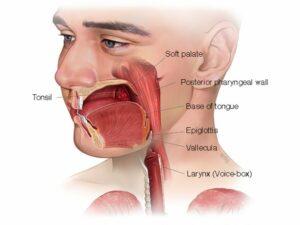
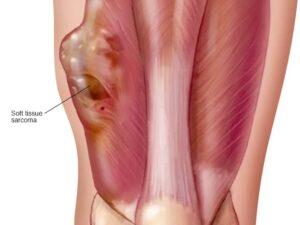
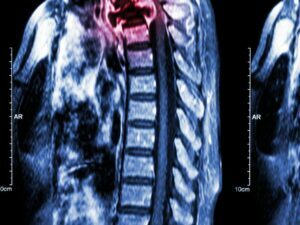
Cancer can manifest in various forms, such as breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and skin cancer. Symptoms and signs depend on the type and location of cancer, often appearing at advanced stages. Early detection through screening and self-examination is crucial, as it significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Cancer treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of cancer and the patient’s overall health. Prevention strategies involve adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to known carcinogens, and participating in recommended screening programs.